Types of Switches – Construction, Working & Applications of Switches
Different Types of Electrical & Mechanical Switches
Table of Contents [Hide]
- 1 What is a Switch?
- 2 Types of Switches
- 3 Types of Mechanical Switches
- 3.1 SPST (Single Pole Single Through)
- 3.2 SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw)
- 3.3 DPST (Double Pole, Single Throw)
- 3.4 DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw)
- 3.5 2P6T (Two Pole, Six Throw)
- 3.6 Intermediate Switch
- 4 Types of Latch and Momentary Operation Switches
- 4.1 Push Buttons Switch
- 4.2 Toggle Switch
- 5 Electrical and Electronic Switches
- 5.1 Transistor as a switch:
- 5.1.1 Typical Circuit of Transistor as a Switch:
- 5.2 Mosfet As a Switch:
- 5.3 Relay as a Switch
- 5.1 Transistor as a switch:
What is a Switch?
In electrical and electronic system, a switch is a device, which can make or break an electrical circuit automatically or manually. In other words, an electrical switch is a controlling device, which interrupt the flow of current or change the direction of current in a circuit. Almost all the electrical and electronics systems contain at least one switch, which is used to make the device ON or OFF. In addition, a switch is used to control the circuit operation and user may able to activate or deactivate the whole or certain parts or process of a connected circuit.

Types of Switches
- SPST (Single Pole Single Through)
- SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw)
- DPST (Double Pole, Single Throw)
- DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw)
- 2P6T (Two Pole, Six Throw)
- Intermediate switch
- Late switch
- Momentary switch
- Push buttons switch
- Toggle switch
- Mosfet switch
- Relay based switch
- Transistor as a switch
- Mechanical, electrical & electronics switches
We will discuss various types of these switches in details given below:
Generally, Switches can be categories as.
- Mechanical Switches
- Electrical/Electronic Switches
Both of these types of switches are widely used in electrical and electronics systems. Switch type selection depends on the system in which they are going to be incorporated. Switches can also be categories on many different bases. We will discuss them one by one later in this article.
Switches can also be categories on the basis of holding the current state.
Latch Switch
The latch switch holds its state whether ON or OFF until the new commands initiated.
Momentary Switch
Momentary switch holds the state only when the specific command is presented only.
Types of Mechanical Switches
Mechanical switch is a switch in which two metal plates touch each other to make a physical contact for the current to flow and separate from each other to interrupt the flow of current. There are many types of Mechanical switches and they are also be categories on the basis of power handling capacity. The contact material is chosen by keeping in mind that the metal oxides, which produced due to corrosion, are mostly insulator and layers of such oxides on the switch plates will hinder the normal operation of the switch.
Mechanical Switches can be categories on the basis of their operation:
SPST (Single Pole Single Through)
This is a simple ON/OFF switch. It is also called as On Way Switch (in the US, they called it Two-Way Switch). When a user press the button of the switch, then the plates of the switch connect with each other and the current starts to flow and vice versa.

Here is the basic construction and working of a SPST (Single Pole Single Through) also known as one way switch.

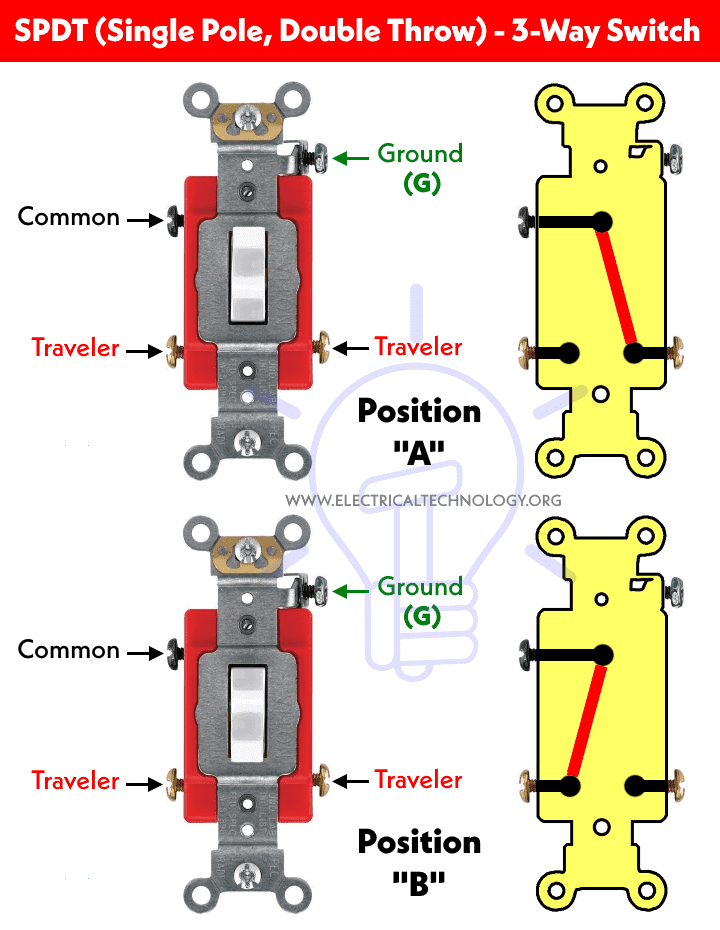
SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw)
This button has three pins in which, one pin is used as common and called a Two-Way Switch (in US, they called it Three-Way Switch). We can send two different signals to same pin by using this switch. Because of this functionality, this switch is also called selector switch.
Other switches related to SPDT are SPCO (Single Pole Changeover) and SPTT (Single Pole Center Off or Single Pole Triple Throw)
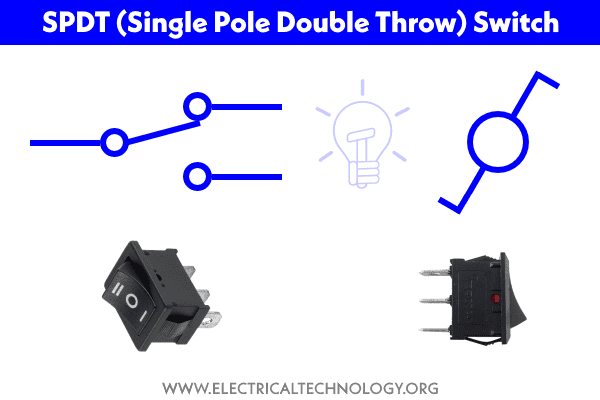
Below is given diagram of construction and operation of Single Pole Double Through (SPDT) switch also known as 2-way switch.
- Related Post: 2 Way Switch – How to Control One Lamp From Two or Three Places by using 2-way switches?
DPST (Double Pole, Single Throw)
This switch is basically two SPST switches in one package and can be operated by a single lever. This switch is mostly used, where we have to break both ground and lines at the same time.
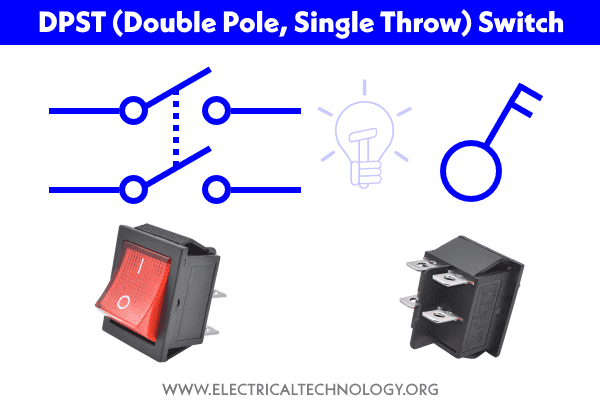
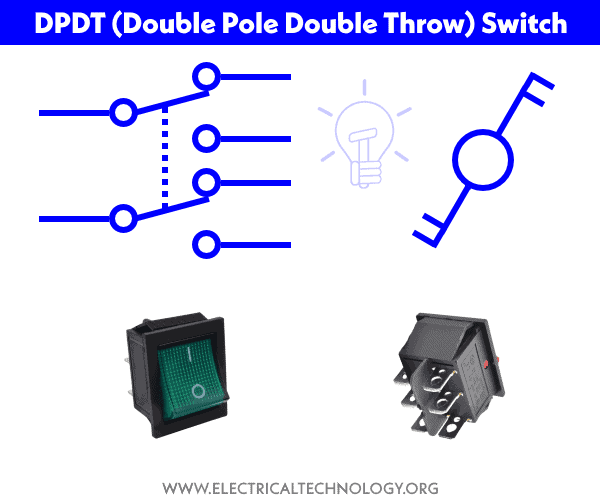
DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw)
This switch is equivalent to two SPDT switches packaged in one pack. This switch has two common pins and four signal pins. Total four different combination of singles can be applied to the input pins of this switch. Another switch, related to DPDT is DPCO (Double Pole Changeover or Double Pole, Centre Off).
2P6T (Two Pole, Six Throw)
It is a type of the changeover switch with a common (COM) which may be connected to six lines with a second two pole switch, which controlling and the operation of the switch is same.

Intermediate Switch
Intermediate switch is Also known as four way switch in the US. We have posted a detailed post about it which can be seen below.
- What is Intermediate Switch – Its Construction, Working & Applications
The figure below shows the basic construction and working principle of intermediate switch.
Types of Latch and Momentary Operation Switches
This button is used in many electronics circuits and can handle a small amount of current. When a user press the button, its metal plate connects with each other, hence the circuit is completed. When the user removes its finger from the button, contact of the pins detached.

Toggle Switch
Toggle switches are actuated by a lever angled in one or more directions. This switch is stable in state and remain in that state unless or until lever is pushed in another direction. Most of all household applications have toggle switch and it can fall into any category as mentioned above e.g. SPST, DPDT etc.

Electrical and Electronic Switches
The Above discussed switches are Mechanical switches and they are user manually operated. Now, we are going to discuss Electrical switches, which are faster in response than mechanical switches and can be switched automatically by an electronic circuit like microcontroller or microprocessor. They can also be categories on the basis of current and voltage rating like mechanical switches.
There are the most widely used electronic switches
- Transistor
- Mosfets
- Relays
The question arises here, why we need electronics switch? The answer of the question is that sometimes, it is necessary that circuit, which makes decision also turn OFF or ON certain devices based on the decision. If only mechanical switch is used, then there should be one person present there all the time to make the device ON and OFF after getting indication message from the circuit. To eliminate this problem, electronics switches are used then. They are very much fast and accurate as compared to mechanical switches. Electronic switches are small in size and do not make noise while switching operation and they make sure the stability and reliability of the system.
Let’s discus types of electronic switches in detail.
Transistor as a switch:
Transistor can be used in different mode of operation but we are going to discuss the transistor as a switch. If we apply a large amount of current at the base of the transistor (keeping in mind the maximum allowed current for the this type of transistor) then we can run this transistor in deep saturation mode i.e. this transistor can be used as a switch.
Typical Circuit of Transistor as a Switch:
No current flowing, when there are 0 volts at the base of Transistor.
When the base is at logic level 1.
Mosfet As a Switch:
Mosfet can also be used for switching purpose at high frequencies. They can operate at Mega hertz frequencies. Mostly, Mosfets used for PWM (pulse width modulation).
Mosfets have three terminals.
- Gate
- Drain
- Source
If we apply logic 1 by keeping in mind the maximum allowed voltage for the base, then the resistance between the drain and source become low and current starts flowing in this channel and vice versa
So lamp would not glow, i.e. it would be Off, when the Gate at logic 0.
Gate at logic 1, lamp is glowing.
Relay as a Switch
A Relay is an electromechanical device, which consists of an electromagnet. When a current is flowing through the coil, it becomes an electromagnet and this electromagnet can be used for switching purposes. Their contacts can fall into any category, e.g. SPDT, DPDT etc. (We will discuss Relay in detail in next posts)
When, we energies the coil, Lamp will glow.

These were the types of switches. We will discuss in detail their construction, operation and application one by one in detail in next coming posts. Thanks.
- Fuse and Types of Fuses
- Basic Electrical Wiring Tutorials
- ELCB, RCB and RCD Circuit Breakers
- Types of Solar Panels
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Working, Types & Uses





Comments
Post a Comment